The SQL LEFT JOIN joins two tables based on a common column. It selects records that have matching values in these columns and the remaining rows from the left table.
Example
-- left join Customers and Orders tables based on their shared customer_id columns
-- Customers is the left table
-- Orders is the right table
SELECT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name, Orders.item
FROM Customers
LEFT JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer_id;Here, the code left joins the Customers and Orders tables based on customer_id, which is common to both tables. The result set contains:
- customer_id and first_name columns from the Customers table (including those whose customer_id value is not present in the
Orderstable) - item column from the
Orderstable
SQL LEFT JOIN Syntax
The syntax of the SQL LEFT JOIN statement is:
SELECT columns_from_both_tables
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column1 = table2.column2
Here,
- table1 is the left table to be joined
- table2 is the right table to be joined
- column1 and column2 are the related columns in the two tables
Example: SQL LEFT Join
-- left join the Customers and Orders tables
SELECT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name, Orders.amount
FROM Customers
LEFT JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer;Here's how this code works:
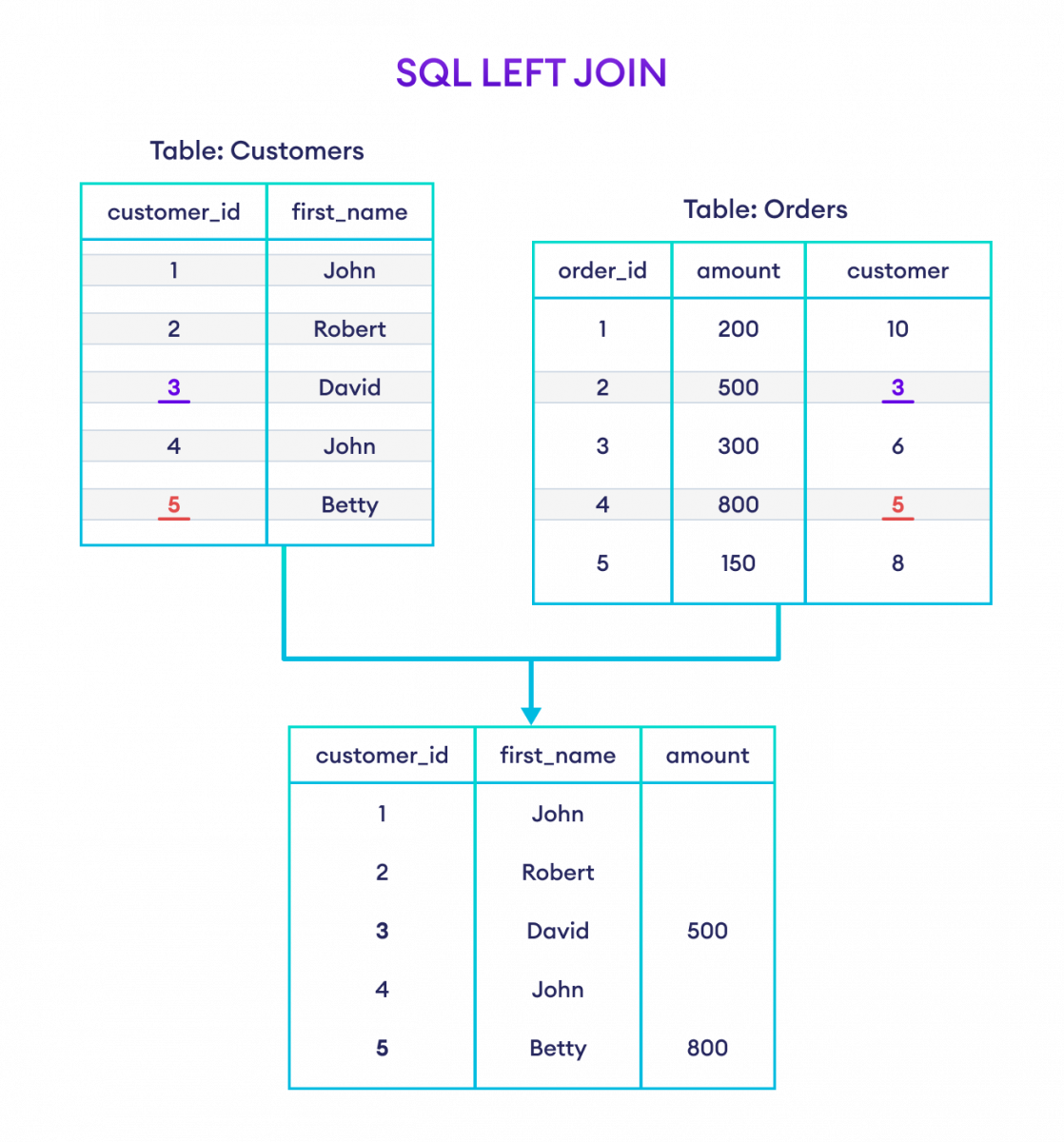
Here, the SQL command selects the customer_id and first_name columns (from the Customers table) and the amount column (from the Orders table).
The result set will contain those rows where there is a match between customer_id (of the Customers table) and customer (of the Orders table), along with all the remaining rows from the Customers table.
LEFT JOIN With WHERE Clause
The SQL LEFT JOIN statement can have an optional WHERE clause. For example,
SELECT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name, Orders.amount
FROM Customers
LEFT JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer
WHERE Orders.amount >= 500;Here, the SQL command joins the Customers and Orders tables and selects rows where the amount is greater than or equal to 500.
SQL LEFT JOIN With AS Alias
We can use AS aliases inside LEFT JOIN to make our query short and clean. For example,
-- use alias C for Categories table
-- use alias P for Products table
SELECT C.cat_name, P.prod_title
FROM Categories AS C
LEFT JOIN Products AS P
ON C.cat_id= P.cat_id;Here, the SQL command left joins the Categories and Products tables while assigning the aliases C and P to them, respectively.
Recommended Readings