The SQL SELECT DISTINCT statement retrieves distinct values from a database table.
Example
-- select the unique ages from the Customers table
SELECT DISTINCT age
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command selects only the unique values of age from the Customers table.
SQL DISTINCT Syntax
The syntax of the SQL DISTINCT statement is:
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2 ...
FROM table;
Here,
column1, column2, ...are the table columnstableis the table name from where we retrieve the distinct columns
For example,
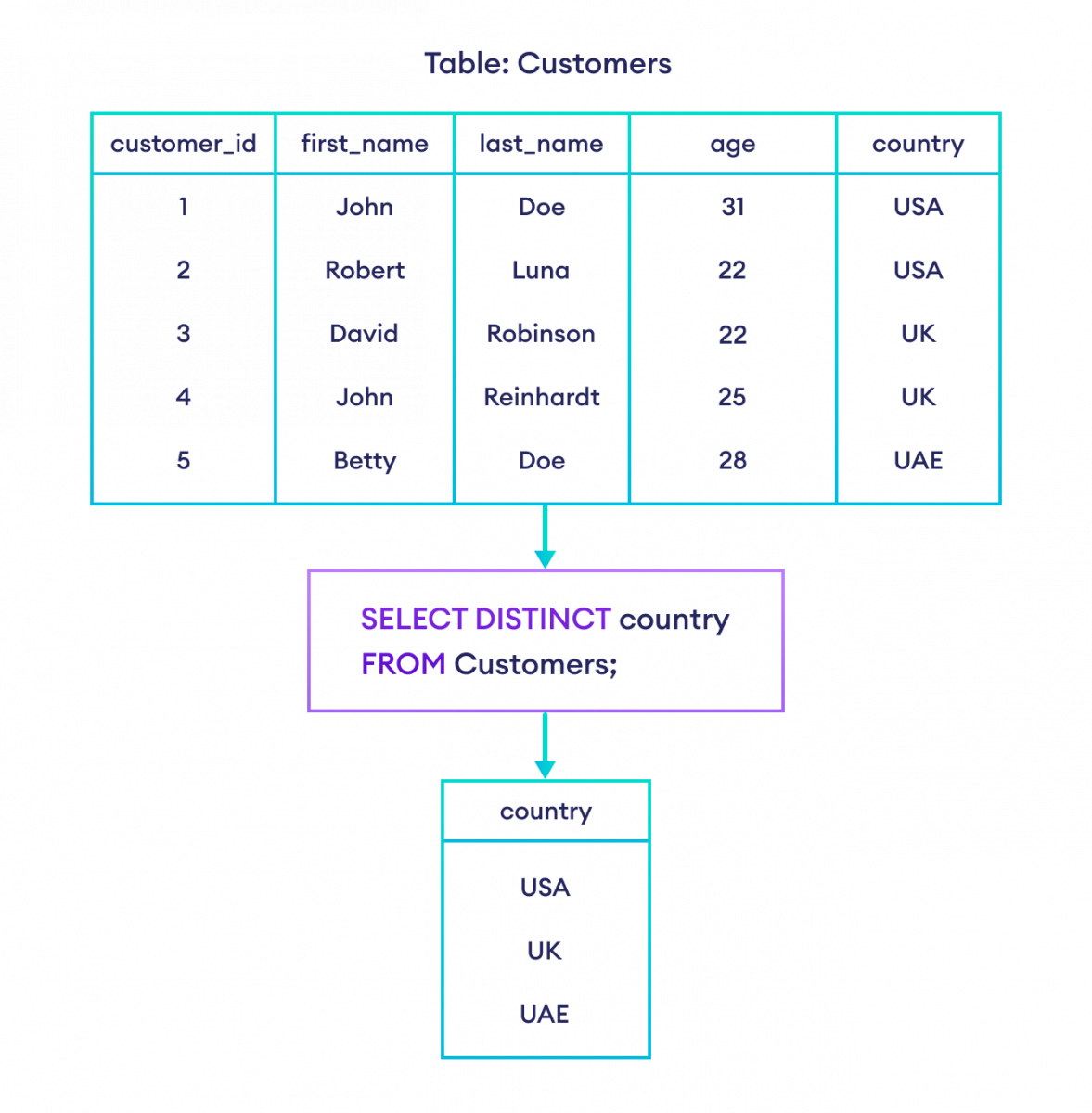
-- select the unique countries from the customers table
SELECT DISTINCT country
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command selects unique countries from the Customers table.
SQL DISTINCT With Multiple Columns
We can also use SELECT DISTINCT with multiple columns.
For example,
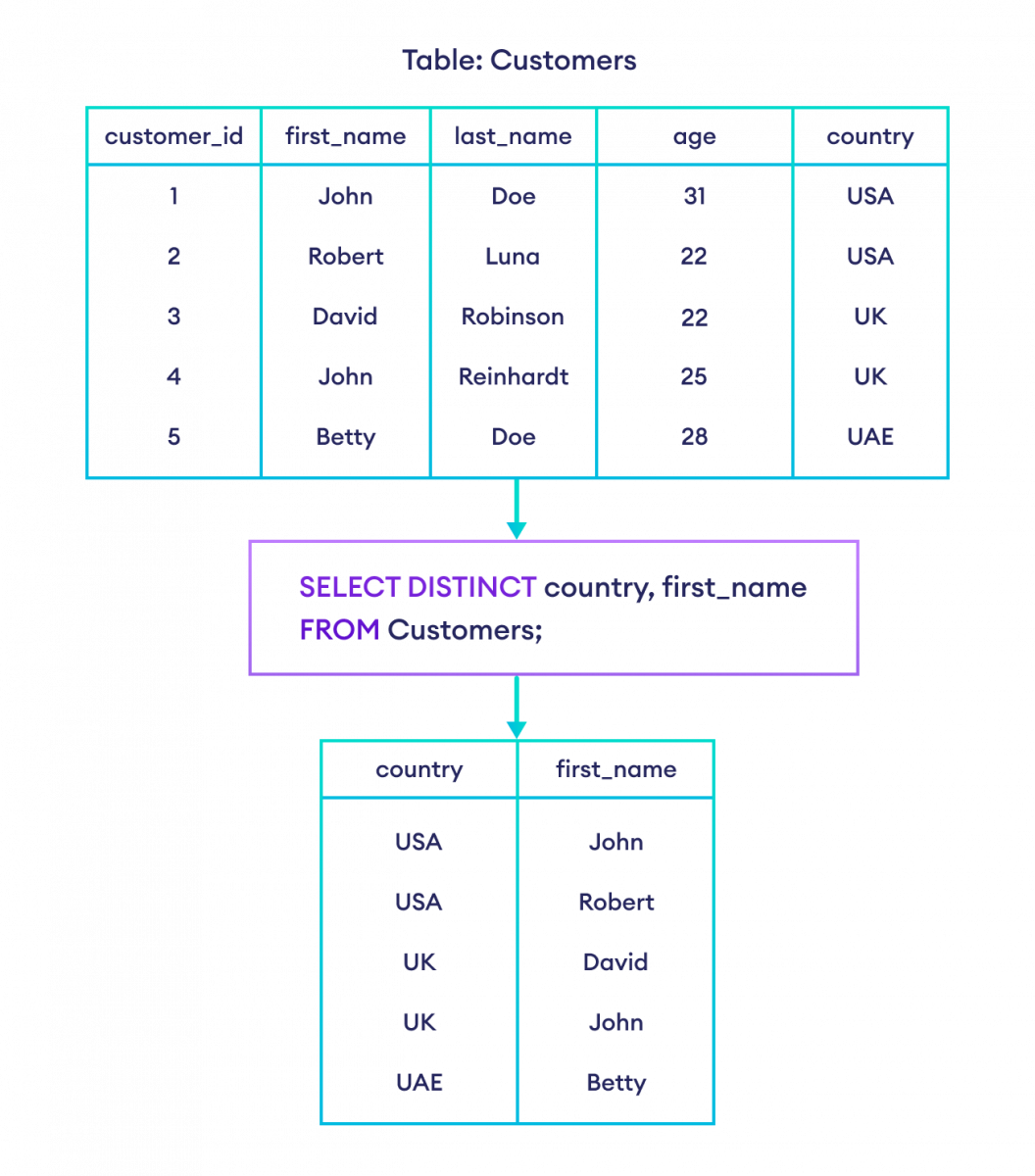
-- select rows if the first name and country of a customer is unique
SELECT DISTINCT country, first_name
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command selects rows if the combination of country and first_name is unique.
DISTINCT With COUNT
If we need to count the number of unique rows, we can use the COUNT() function with DISTINCT.
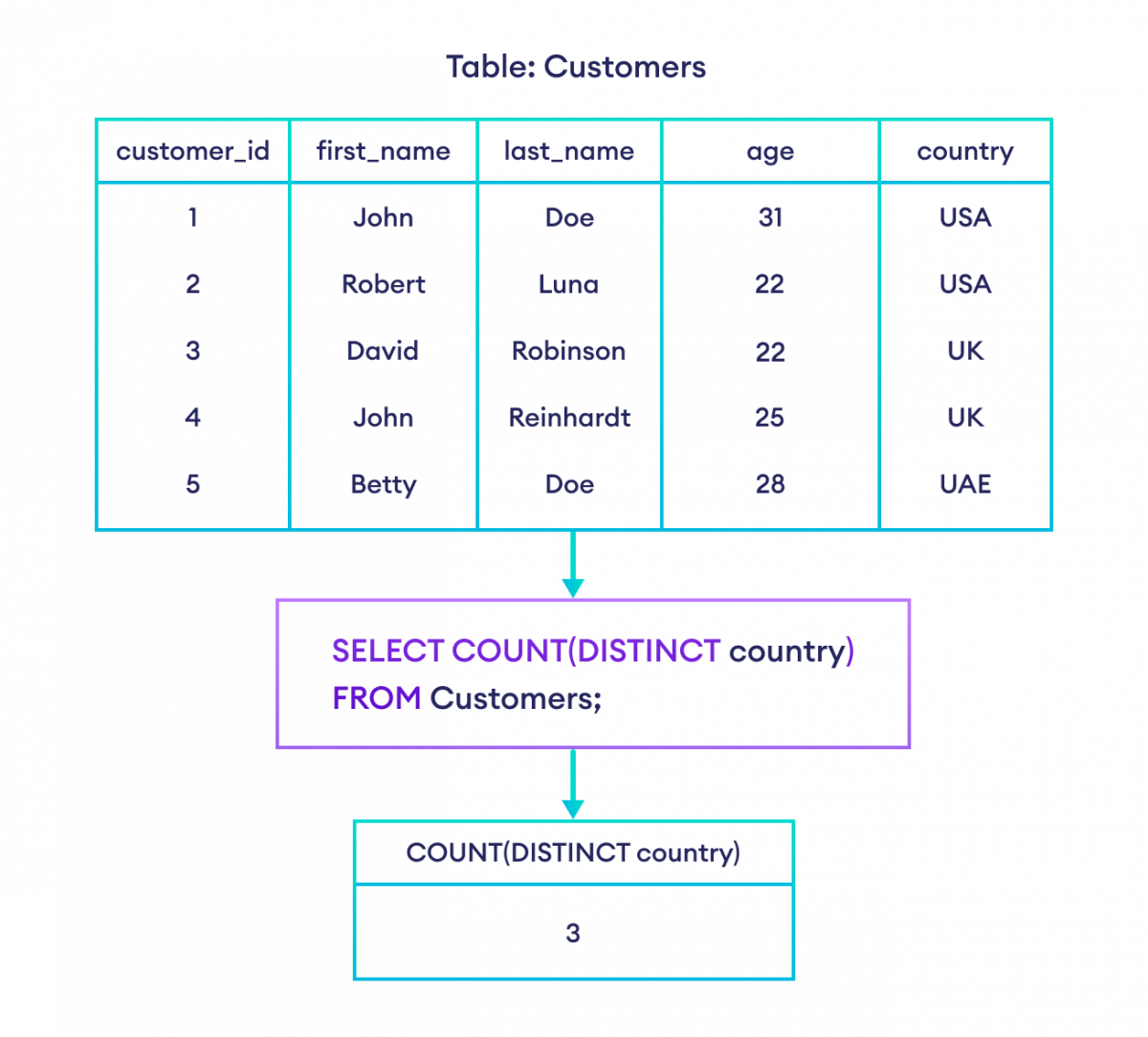
-- count the unique countries where customers are from
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT country)
FROM Customers;Here, the SQL command returns the count of unique countries.
To learn more, visit SQL COUNT().
More SQL DISTINCT Examples
Let's take a look at an example,
-- with distinct
SELECT DISTINCT country
FROM Customers;
-- with group by
SELECT country
FROM Customers
GROUP BY country;
Here, both of the SQL commands are similar and return unique countries from the Customers table.
To learn more, visit SQL GROUP BY.
Let's take a look at an example,
-- with order by
SELECT DISTINCT age
FROM Customers
ORDER BY age DESC;
Here, the SQL command selects unique ages and orders them in descending order from the Customers table.
To learn more, visit SQL ORDER BY.