A Queue<T> is a generic class that arranges elements of a specified data type using First In First Out (FIFO) principles. For example,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// create a queue
Queue<string> fruits = new Queue<string>();
// adds "Apple" and "Orange" to the queue
fruits.Enqueue("Apple");
fruits.Enqueue("Orange");
// print elements of the queue
foreach (string item in fruits)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
Output
Apple Orange
Here, fruits is a queue that contains string elements ("Apple" and "Orange").
We will learn about Queue<T> in detail.
Queue Implementation
In the queue, elements are stored and accessed in First In First Out (FIFO) manner. That is, elements that are added first will be removed first.
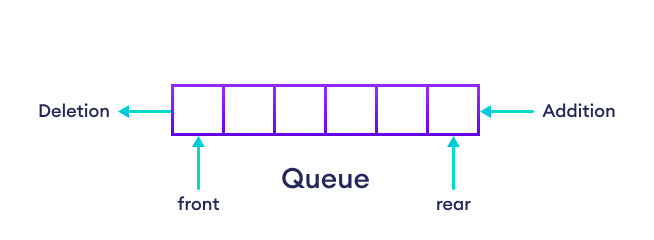
Create a Queue in C#
To create Queue<T> in C#, we need to use the System.Collection.Generic namespace. Here is how we can create Queue<T> in C#,
Queue<dataType> queueName = new Queue<dataType>();
Here, dataType indicates the queue's type. For example,
// create integer type stack
Queue<int> queue1 = new Queue<int>();
// create string type stack
Queue<string> queue2 = new Queue<string>();
C# Queue Methods
C# provides 3 major Queue<T> methods. These methods are:
Enqueue()- adds an element to the end of the queueDequeue()- removes and returns an element from the beginning of the queuePeek()- returns an element from the beginning of the queue without removing
Let's learn each method in detail.
Queue Enqueue() Method
To add an element to the end of the queue, we use the Enqueue() method. For example,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// create a queue
Queue<int> numbers = new Queue<int>();
// adds 65 and 17 to the queue
numbers.Enqueue(65);
numbers.Enqueue(17);
// print elements of the queue
foreach (int item in numbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
Output
65 17
In the above example, we have created Queue<T> class named numbers.
Then we added elements to the queue using the Enqueue() method.
numbers.Enqueue(65)- adds 65 to the queuenumbers.Enqueue(17)- adds 17 to the queue
We then printed those elements using a foreach loop.
Since the queue follows FIFO principle, the element added at the first (65) is displayed at the first in the output.
Queue Dequeue() Method
To remove an element from the beginning of the queue, we use the Dequeue() method. For example,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// create a queue
Queue<string> colors = new Queue<string>();
// adds "Red" and "Blue" to the queue
colors.Enqueue("Red");
colors.Enqueue("Blue");
// removes element from the beginning of the colors queue
var removedElement = colors.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine("Removed Element: " + removedElement);
}
}
Output
Removed Element: Red
In the above example, we have used the Dequeue() method to remove an element from the colors queue.
The method removed and returned "Red" from the beginning of the queue.
Queue Peek() Method
The Peek() method returns the element from the beginning of the queue without removing it. For example,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// create a queue
Queue<string> planet = new Queue<string>();
// adds "Earth" and "Jupiter" to the queue
planet.Enqueue("Earth");
planet.Enqueue("Jupiter");
// returns element from the beginning of the planet queue
Console.WriteLine("Element at beginning of queue: " + planet.Peek());
}
}
Output
Element at beginning of queue: Earth
Here, we have displayed the element present at the beginning of the planet queue using the Peek() method.
Check Whether an Element is Present Inside a Queue
We can use the Contains() method to check whether an element is present inside the queue or not.
The method returns True if a specified element exists in the queue. If not it returns False. For example,
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// create a queue
Queue<string> planet = new Queue<string>();
// adds "Earth" and "Jupiter" to the queue
planet.Enqueue("Earth");
planet.Enqueue("Jupiter");
// check if queue contains "Mars"
Console.WriteLine(planet.Contains("Mars"));
// check if queue contains "Jupiter"
Console.WriteLine(planet.Contains("Jupiter"));
}
}
Output
False True