A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this way is known as recursion.
A physical world example would be to place two parallel mirrors facing each other. Any object in between them would be reflected recursively.
How Recursion Works?
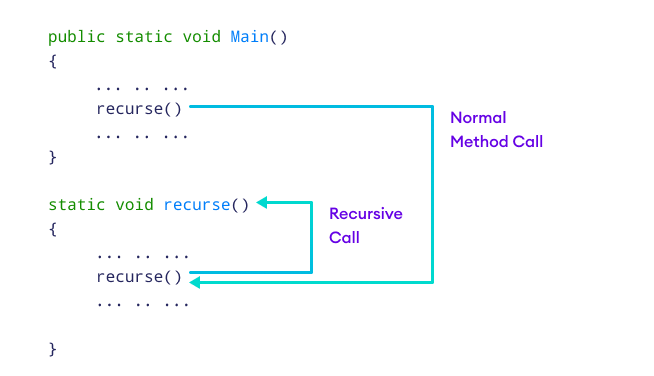
In the above example, we have called the recurse() method from inside the Main method (normal method call). And, inside the recurse() method, we are again calling the same recurse() method. This is a recursive call.
To stop the recursive call, we need to provide some conditions inside the method. Otherwise, the method will be called infinitely.
Hence, we use the if...else statement (or similar approach) to terminate the recursive call inside the method.
Example: Factorial of a Number Using Recursion
The factorial of a positive number n is given by:
factorial of n (n!) = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4....n
In C#, we can use recursion to find the factorial of a number. For example,
using System;
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int fact, num;
Console.Write("Enter a number: ");
// take input from user
num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Program obj = new Program();
// calling recursive function
fact = obj.factorial(num);
Console.WriteLine("Factorial of {0} is {1}", num, fact);
}
// recursive function
public int factorial(int num)
{
// termination condition
if (num == 0)
return 1;
else
// recursive call
return num * factorial(num - 1);
}
}
Output
Enter a number: 4 Factorial of 4 is 24
In the above example, we have a method named factorial(). We have passed a variable num as an argument in factorial().
The factorial() is called from the Main() method. Inside factorial(), notice the statement:
return num * factorial(num - 1);
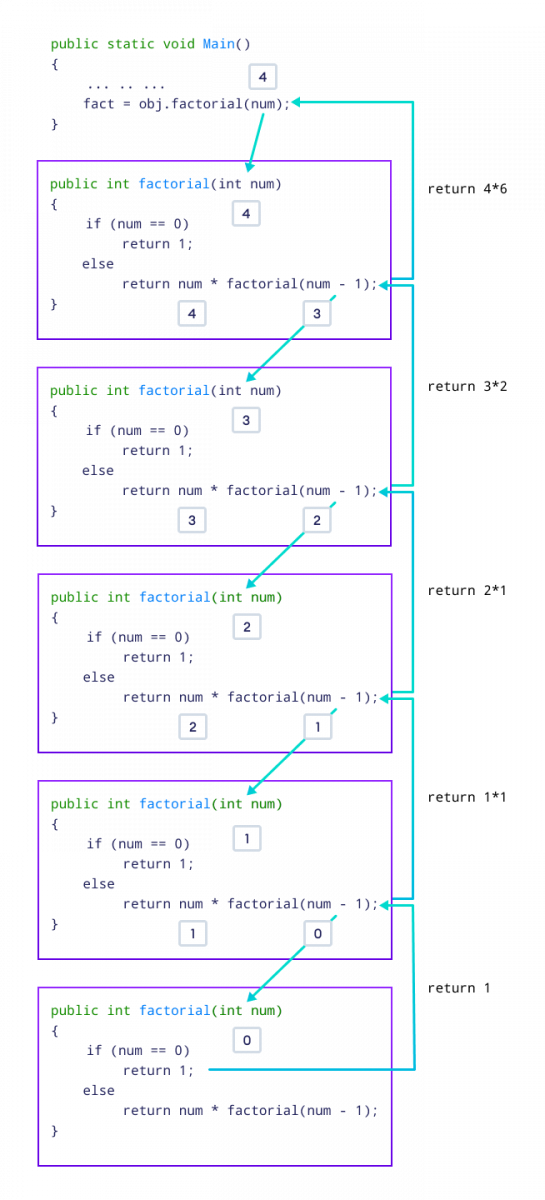
Here, the factorial() method is calling itself. Initially, the value of num inside factorial() is 4. During the next recursive call, 3 is passed to the factorial() method. This process continues until num is equal to 0.
When num is equal to 0, the if statement returns true hence 1 is returned. Finally, the accumulated result is passed to the Main() method.
Working of Factorial Program
The image below will give you a better idea of how the factorial program is executed using recursion.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion
Advantage - Using recursion, our code looks clean and more readable.
Disadvantages - When a recursive call is made, new storage locations for variables are allocated on the stack. As each recursive call returns, the old variables and parameters are removed from the stack. Hence, recursion generally uses more memory and is generally slow.