A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
Working of Recursion in C++
void recurse()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
int main()
{
... .. ...
recurse();
... .. ...
}
The figure below shows how recursion works by calling itself over and over again.
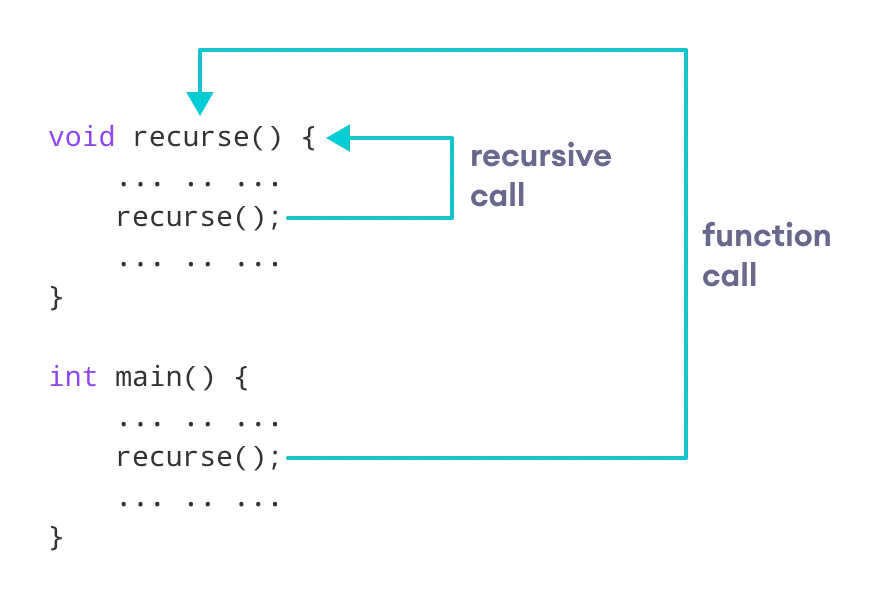
The recursion continues until some condition is met.
To prevent infinite recursion, if...else statement (or similar approach) can be used where one branch makes the recursive call and the other doesn't.
Example 1: Factorial of a Number Using Recursion
// Factorial of n = 1*2*3*...*n
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int factorial(int);
int main() {
int n, result;
cout << "Enter a non-negative number: ";
cin >> n;
result = factorial(n);
cout << "Factorial of " << n << " = " << result;
return 0;
}
int factorial(int n) {
if (n > 1) {
return n * factorial(n - 1);
} else {
return 1;
}
}
Output
Enter a non-negative number: 4 Factorial of 4 = 24
Working of Factorial Program
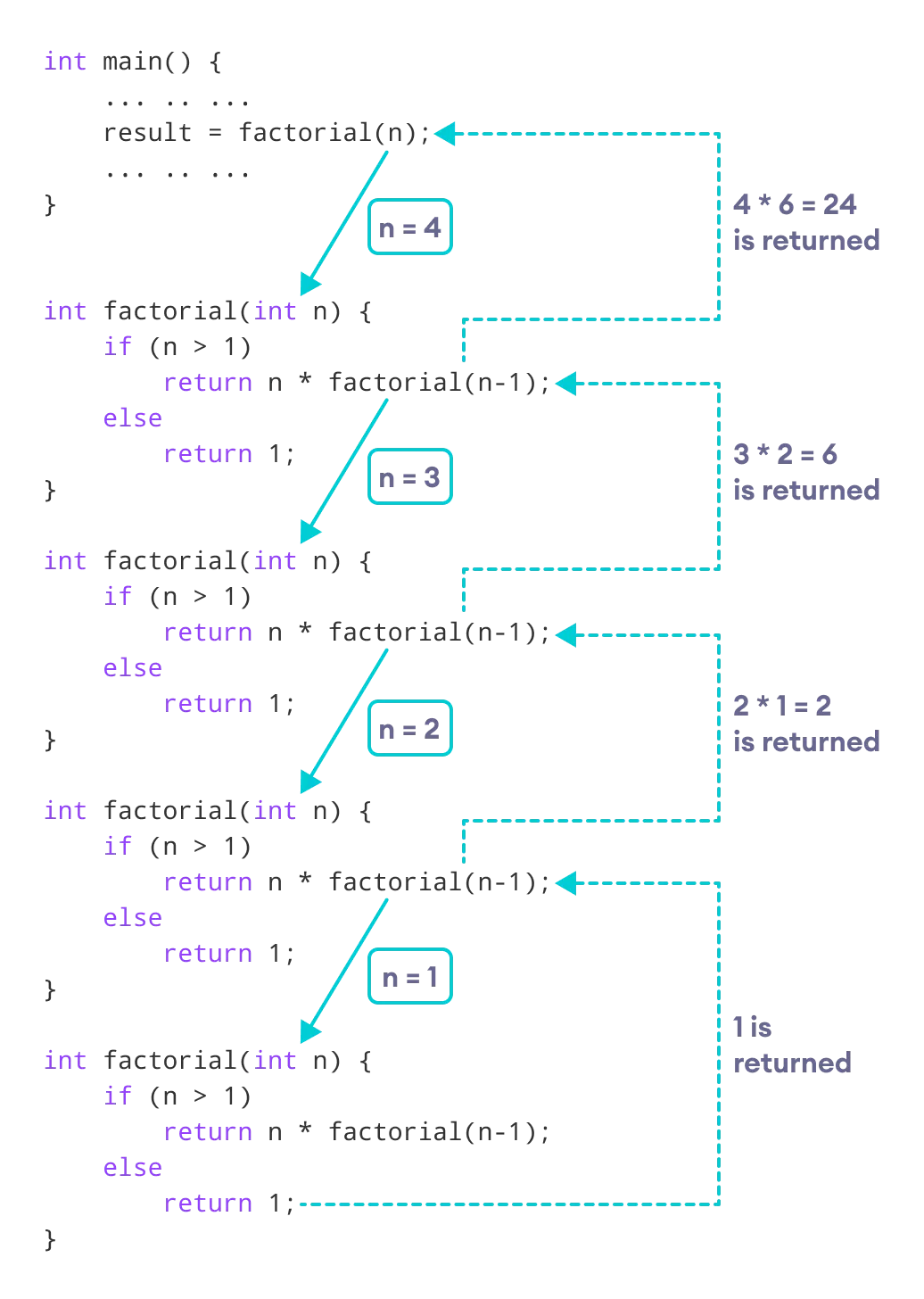
As we can see, the factorial() function is calling itself. However, during each call, we have decreased the value of n by 1. When n is less than 1, the factorial() function ultimately returns the output.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion
Below are the pros and cons of using recursion in C++.
Advantages of C++ Recursion
- It makes our code shorter and cleaner.
- Recursion is required in problems concerning data structures and advanced algorithms, such as Graph and Tree Traversal.
Disadvantages of C++ Recursion
- It takes a lot of stack space compared to an iterative program.
- It uses more processor time.
- It can be more difficult to debug compared to an equivalent iterative program.