Example: Implement Graph Data Structure
class Graph {
// inner class
// to keep track of edges
class Edge {
int src, dest;
}
// number of vertices and edges
int vertices, edges;
// array to store all edges
Edge[] edge;
Graph(int vertices, int edges) {
this.vertices = vertices;
this.edges = edges;
// initialize the edge array
edge = new Edge[edges];
for(int i = 0; i < edges; i++) {
// each element of the edge array
// is an object of Edge type
edge[i] = new Edge();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of Graph class
int noVertices = 5;
int noEdges = 8;
Graph g = new Graph(noVertices, noEdges);
// create graph
g.edge[0].src = 1; // edge 1---2
g.edge[0].dest = 2;
g.edge[1].src = 1; // edge 1---3
g.edge[1].dest = 3;
g.edge[2].src = 1; // edge 1---4
g.edge[2].dest = 4;
g.edge[3].src = 2; // edge 2---4
g.edge[3].dest = 4;
g.edge[4].src = 2; // edge 2---5
g.edge[4].dest = 5;
g.edge[5].src = 3; // edge 3---4
g.edge[5].dest = 4;
g.edge[6].src = 3; // edge 3---5
g.edge[6].dest = 5;
g.edge[7].src = 4; // edge 4---5
g.edge[7].dest = 5;
// print graph
for(int i = 0; i < noEdges; i++) {
System.out.println(g.edge[i].src + " - " + g.edge[i].dest);
}
}
}
Output
1 - 2 1 - 3 1 - 4 2 - 4 2 - 5 3 - 4 3 - 5 4 - 5
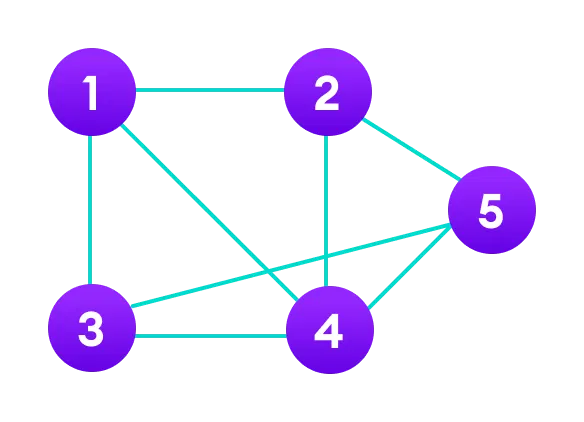
In the above example, we have implemented the graph data structure in Java. To learn more about graphs, visit Graph Data Structure.